Generates random deviates from the two-parameter Kumaraswamy (Kw)
distribution with shape parameters alpha (\(\alpha\)) and
beta (\(\beta\)).
Value
A vector of length n containing random deviates from the Kw
distribution, with values in (0, 1). The length of the result is determined
by n and the recycling rule applied to the parameters (alpha,
beta). Returns NaN if parameters are invalid (e.g.,
alpha <= 0, beta <= 0).
Details
The generation method uses the inverse transform (quantile) method.
That is, if \(U\) is a random variable following a standard Uniform
distribution on (0, 1), then \(X = Q(U)\) follows the Kw distribution,
where \(Q(p)\) is the Kw quantile function (qkw):
$$
Q(p) = \left\{ 1 - (1 - p)^{1/\beta} \right\}^{1/\alpha}
$$
The implementation generates \(U\) using runif
and applies this transformation. This is equivalent to the general GKw
generation method (rgkw) evaluated at \(\gamma=1, \delta=0, \lambda=1\).
References
Kumaraswamy, P. (1980). A generalized probability density function for double-bounded random processes. Journal of Hydrology, 46(1-2), 79-88.
Jones, M. C. (2009). Kumaraswamy's distribution: A beta-type distribution with some tractability advantages. Statistical Methodology, 6(1), 70-81.
Devroye, L. (1986). Non-Uniform Random Variate Generation. Springer-Verlag. (General methods for random variate generation).
Examples
# \donttest{
set.seed(2029) # for reproducibility
# Generate 1000 random values from a specific Kw distribution
alpha_par <- 2.0
beta_par <- 3.0
x_sample_kw <- rkw(1000, alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par)
summary(x_sample_kw)
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 0.01825 0.29985 0.45247 0.45264 0.58978 0.93608
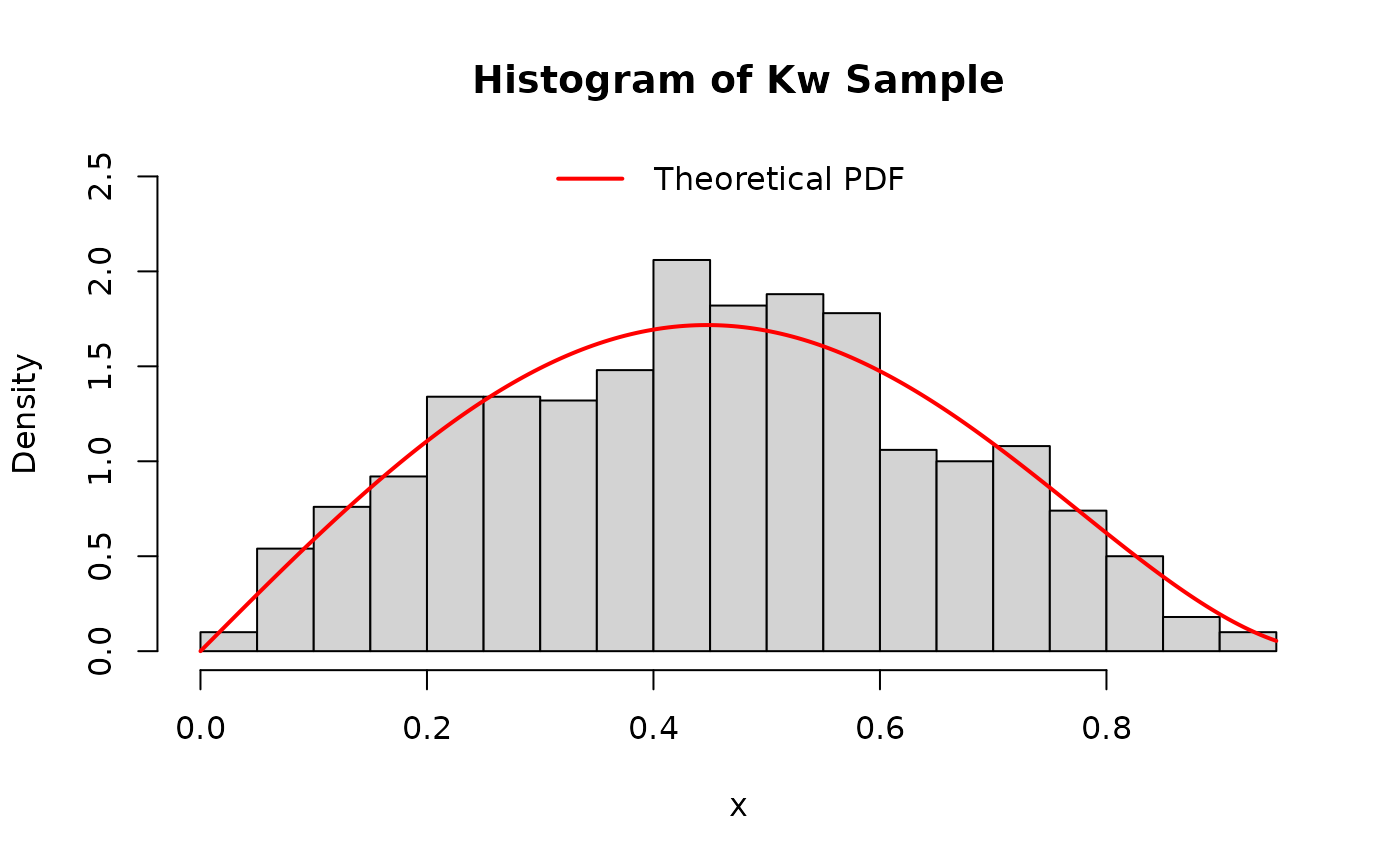
# Histogram of generated values compared to theoretical density
hist(x_sample_kw,
breaks = 30, freq = FALSE, # freq=FALSE for density
main = "Histogram of Kw Sample", xlab = "x", ylim = c(0, 2.5)
)
curve(dkw(x, alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par),
add = TRUE, col = "red", lwd = 2, n = 201
)
legend("top", legend = "Theoretical PDF", col = "red", lwd = 2, bty = "n")
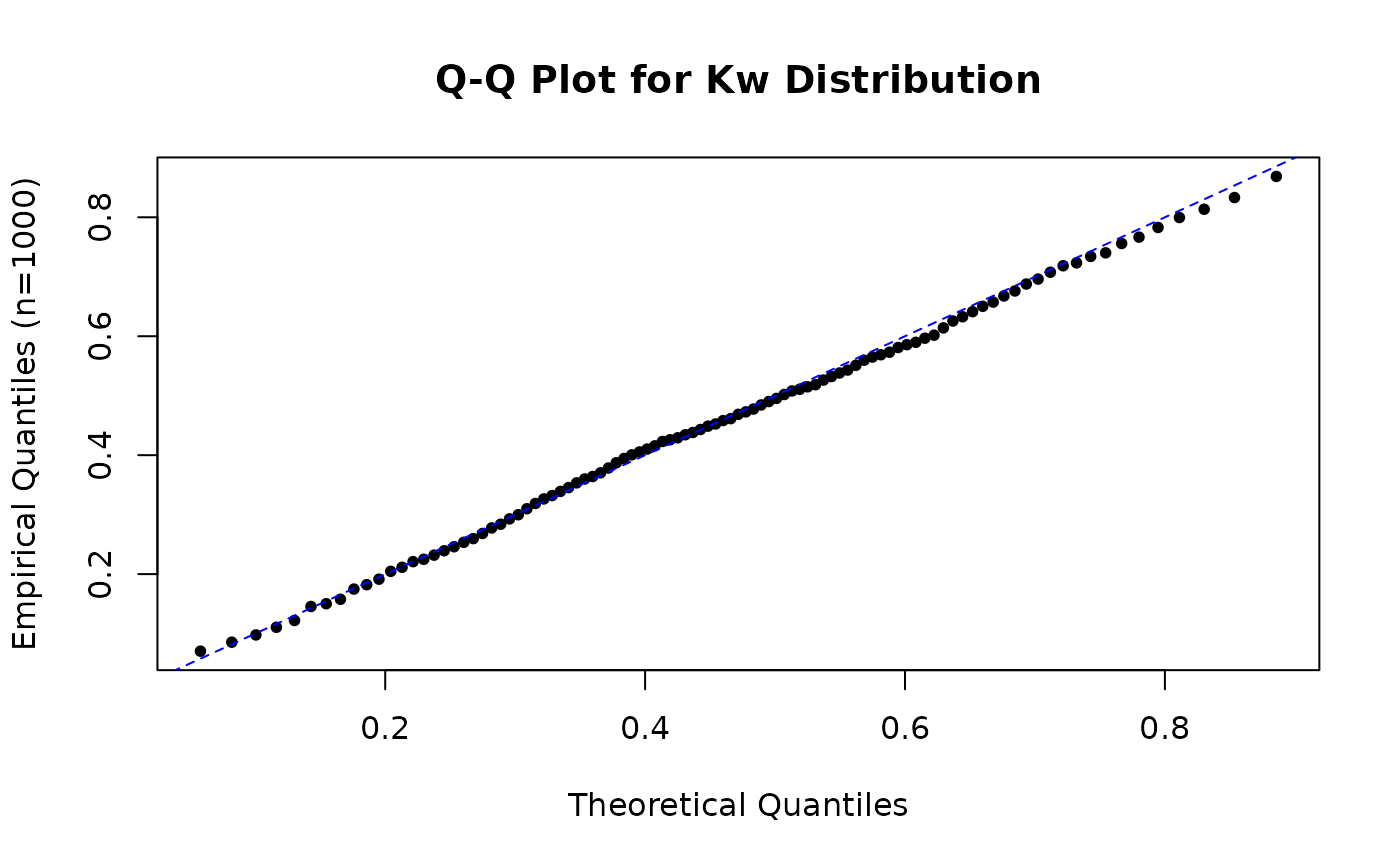
 # Comparing empirical and theoretical quantiles (Q-Q plot)
prob_points <- seq(0.01, 0.99, by = 0.01)
theo_quantiles <- qkw(prob_points, alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par)
emp_quantiles <- quantile(x_sample_kw, prob_points, type = 7)
plot(theo_quantiles, emp_quantiles,
pch = 16, cex = 0.8,
main = "Q-Q Plot for Kw Distribution",
xlab = "Theoretical Quantiles", ylab = "Empirical Quantiles (n=1000)"
)
abline(a = 0, b = 1, col = "blue", lty = 2)
# Comparing empirical and theoretical quantiles (Q-Q plot)
prob_points <- seq(0.01, 0.99, by = 0.01)
theo_quantiles <- qkw(prob_points, alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par)
emp_quantiles <- quantile(x_sample_kw, prob_points, type = 7)
plot(theo_quantiles, emp_quantiles,
pch = 16, cex = 0.8,
main = "Q-Q Plot for Kw Distribution",
xlab = "Theoretical Quantiles", ylab = "Empirical Quantiles (n=1000)"
)
abline(a = 0, b = 1, col = "blue", lty = 2)
 # Compare summary stats with rgkw(..., gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1)
# Note: individual values will differ due to randomness
x_sample_gkw <- rgkw(1000,
alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par, gamma = 1.0,
delta = 0.0, lambda = 1.0
)
print("Summary stats for rkw sample:")
#> [1] "Summary stats for rkw sample:"
print(summary(x_sample_kw))
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 0.01825 0.29985 0.45247 0.45264 0.58978 0.93608
print("Summary stats for rgkw(gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1) sample:")
#> [1] "Summary stats for rgkw(gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1) sample:"
print(summary(x_sample_gkw)) # Should be similar
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 0.00568 0.30017 0.45069 0.45469 0.59646 0.95381
# }
# Compare summary stats with rgkw(..., gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1)
# Note: individual values will differ due to randomness
x_sample_gkw <- rgkw(1000,
alpha = alpha_par, beta = beta_par, gamma = 1.0,
delta = 0.0, lambda = 1.0
)
print("Summary stats for rkw sample:")
#> [1] "Summary stats for rkw sample:"
print(summary(x_sample_kw))
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 0.01825 0.29985 0.45247 0.45264 0.58978 0.93608
print("Summary stats for rgkw(gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1) sample:")
#> [1] "Summary stats for rgkw(gamma=1, delta=0, lambda=1) sample:"
print(summary(x_sample_gkw)) # Should be similar
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 0.00568 0.30017 0.45069 0.45469 0.59646 0.95381
# }