Computes the negative log-likelihood function for the Kumaraswamy-Kumaraswamy
(kkw) distribution with parameters alpha (\(\alpha\)), beta
(\(\beta\)), delta (\(\delta\)), and lambda (\(\lambda\)),
given a vector of observations. This distribution is a special case of the
Generalized Kumaraswamy (GKw) distribution where \(\gamma = 1\).
Value
Returns a single double value representing the negative
log-likelihood (\(-\ell(\theta|\mathbf{x})\)). Returns Inf
if any parameter values in par are invalid according to their
constraints, or if any value in data is not in the interval (0, 1).
Details
The kkw distribution is the GKw distribution (dgkw) with \(\gamma=1\).
Its probability density function (PDF) is:
$$
f(x | \theta) = (\delta + 1) \lambda \alpha \beta x^{\alpha - 1} (1 - x^\alpha)^{\beta - 1} \bigl[1 - (1 - x^\alpha)^\beta\bigr]^{\lambda - 1} \bigl\{1 - \bigl[1 - (1 - x^\alpha)^\beta\bigr]^\lambda\bigr\}^{\delta}
$$
for \(0 < x < 1\) and \(\theta = (\alpha, \beta, \delta, \lambda)\).
The log-likelihood function \(\ell(\theta | \mathbf{x})\) for a sample
\(\mathbf{x} = (x_1, \dots, x_n)\) is \(\sum_{i=1}^n \ln f(x_i | \theta)\):
$$
\ell(\theta | \mathbf{x}) = n[\ln(\delta+1) + \ln(\lambda) + \ln(\alpha) + \ln(\beta)]
+ \sum_{i=1}^{n} [(\alpha-1)\ln(x_i) + (\beta-1)\ln(v_i) + (\lambda-1)\ln(w_i) + \delta\ln(z_i)]
$$
where:
\(v_i = 1 - x_i^{\alpha}\)
\(w_i = 1 - v_i^{\beta} = 1 - (1-x_i^{\alpha})^{\beta}\)
\(z_i = 1 - w_i^{\lambda} = 1 - [1-(1-x_i^{\alpha})^{\beta}]^{\lambda}\)
This function computes and returns the negative log-likelihood, \(-\ell(\theta|\mathbf{x})\),
suitable for minimization using optimization routines like optim.
Numerical stability is maintained similarly to llgkw.
References
Cordeiro, G. M., & de Castro, M. (2011). A new family of generalized distributions. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation,
Kumaraswamy, P. (1980). A generalized probability density function for double-bounded random processes. Journal of Hydrology, 46(1-2), 79-88.
Examples
# \donttest{
## Example 1: Basic Log-Likelihood Evaluation
# Generate sample data
set.seed(123)
n <- 1000
true_params <- c(alpha = 2.0, beta = 3.0, delta = 1.5, lambda = 2.0)
data <- rkkw(n,
alpha = true_params[1], beta = true_params[2],
delta = true_params[3], lambda = true_params[4]
)
# Evaluate negative log-likelihood at true parameters
nll_true <- llkkw(par = true_params, data = data)
cat("Negative log-likelihood at true parameters:", nll_true, "\n")
#> Negative log-likelihood at true parameters: -586.4032
# Evaluate at different parameter values
test_params <- rbind(
c(1.5, 2.5, 1.0, 1.5),
c(2.0, 3.0, 1.5, 2.0),
c(2.5, 3.5, 2.0, 2.5)
)
nll_values <- apply(test_params, 1, function(p) llkkw(p, data))
results <- data.frame(
Alpha = test_params[, 1],
Beta = test_params[, 2],
Delta = test_params[, 3],
Lambda = test_params[, 4],
NegLogLik = nll_values
)
print(results, digits = 4)
#> Alpha Beta Delta Lambda NegLogLik
#> 1 1.5 2.5 1.0 1.5 -390.1
#> 2 2.0 3.0 1.5 2.0 -586.4
#> 3 2.5 3.5 2.0 2.5 -368.5
## Example 2: Maximum Likelihood Estimation
# Optimization using BFGS with analytical gradient
fit <- optim(
par = c(1.5, 2.5, 1.0, 1.5),
fn = llkkw,
gr = grkkw,
data = data,
method = "BFGS",
hessian = TRUE
)
mle <- fit$par
names(mle) <- c("alpha", "beta", "delta", "lambda")
se <- sqrt(diag(solve(fit$hessian)))
results <- data.frame(
Parameter = c("alpha", "beta", "delta", "lambda"),
True = true_params,
MLE = mle,
SE = se,
CI_Lower = mle - 1.96 * se,
CI_Upper = mle + 1.96 * se
)
print(results, digits = 4)
#> Parameter True MLE SE CI_Lower CI_Upper
#> alpha alpha 2.0 2.304 2.170 -1.950 6.558
#> beta beta 3.0 3.610 8.426 -12.905 20.124
#> delta delta 1.5 1.222 4.811 -8.206 10.651
#> lambda lambda 2.0 1.705 1.685 -1.598 5.007
cat("\nNegative log-likelihood at MLE:", fit$value, "\n")
#>
#> Negative log-likelihood at MLE: -586.5422
cat("AIC:", 2 * fit$value + 2 * length(mle), "\n")
#> AIC: -1165.084
cat("BIC:", 2 * fit$value + length(mle) * log(n), "\n")
#> BIC: -1145.453
## Example 3: Comparing Optimization Methods
methods <- c("BFGS", "L-BFGS-B", "Nelder-Mead", "CG")
start_params <- c(1.5, 2.5, 1.0, 1.5)
comparison <- data.frame(
Method = character(),
Alpha = numeric(),
Beta = numeric(),
Delta = numeric(),
Lambda = numeric(),
NegLogLik = numeric(),
Convergence = integer(),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
for (method in methods) {
if (method %in% c("BFGS", "CG")) {
fit_temp <- optim(
par = start_params,
fn = llkkw,
gr = grkkw,
data = data,
method = method
)
} else if (method == "L-BFGS-B") {
fit_temp <- optim(
par = start_params,
fn = llkkw,
gr = grkkw,
data = data,
method = method,
lower = c(0.01, 0.01, 0.01, 0.01),
upper = c(100, 100, 100, 100)
)
} else {
fit_temp <- optim(
par = start_params,
fn = llkkw,
data = data,
method = method
)
}
comparison <- rbind(comparison, data.frame(
Method = method,
Alpha = fit_temp$par[1],
Beta = fit_temp$par[2],
Delta = fit_temp$par[3],
Lambda = fit_temp$par[4],
NegLogLik = fit_temp$value,
Convergence = fit_temp$convergence,
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
))
}
print(comparison, digits = 4, row.names = FALSE)
#> Method Alpha Beta Delta Lambda NegLogLik Convergence
#> BFGS 2.304 3.610 1.222 1.705 -586.5 0
#> L-BFGS-B 2.102 2.937 1.697 1.873 -586.5 0
#> Nelder-Mead 2.385 3.957 1.043 1.644 -586.5 0
#> CG 2.003 2.974 1.578 2.002 -586.5 1
## Example 4: Likelihood Ratio Test
# Test H0: delta = 1.5 vs H1: delta free
loglik_full <- -fit$value
restricted_ll <- function(params_restricted, data, delta_fixed) {
llkkw(par = c(
params_restricted[1], params_restricted[2],
delta_fixed, params_restricted[3]
), data = data)
}
fit_restricted <- optim(
par = c(mle[1], mle[2], mle[4]),
fn = restricted_ll,
data = data,
delta_fixed = 1.5,
method = "BFGS"
)
loglik_restricted <- -fit_restricted$value
lr_stat <- 2 * (loglik_full - loglik_restricted)
p_value <- pchisq(lr_stat, df = 1, lower.tail = FALSE)
cat("LR Statistic:", round(lr_stat, 4), "\n")
#> LR Statistic: 0.0066
cat("P-value:", format.pval(p_value, digits = 4), "\n")
#> P-value: 0.9352
## Example 5: Univariate Profile Likelihoods
# Profile for alpha
alpha_grid <- seq(mle[1] - 1, mle[1] + 1, length.out = 40)
alpha_grid <- alpha_grid[alpha_grid > 0]
profile_ll_alpha <- numeric(length(alpha_grid))
for (i in seq_along(alpha_grid)) {
profile_fit <- optim(
par = mle[-1],
fn = function(p) llkkw(c(alpha_grid[i], p), data),
method = "Nelder-Mead"
)
profile_ll_alpha[i] <- -profile_fit$value
}
# Profile for beta
beta_grid <- seq(mle[2] - 1, mle[2] + 1, length.out = 40)
beta_grid <- beta_grid[beta_grid > 0]
profile_ll_beta <- numeric(length(beta_grid))
for (i in seq_along(beta_grid)) {
profile_fit <- optim(
par = mle[-2],
fn = function(p) llkkw(c(p[1], beta_grid[i], p[2], p[3]), data),
method = "Nelder-Mead"
)
profile_ll_beta[i] <- -profile_fit$value
}
# Profile for delta
delta_grid <- seq(mle[3] - 0.8, mle[3] + 0.8, length.out = 40)
delta_grid <- delta_grid[delta_grid > 0]
profile_ll_delta <- numeric(length(delta_grid))
for (i in seq_along(delta_grid)) {
profile_fit <- optim(
par = mle[-3],
fn = function(p) llkkw(c(p[1], p[2], delta_grid[i], p[3]), data),
method = "Nelder-Mead"
)
profile_ll_delta[i] <- -profile_fit$value
}
# Profile for lambda
lambda_grid <- seq(mle[4] - 1, mle[4] + 1, length.out = 40)
lambda_grid <- lambda_grid[lambda_grid > 0]
profile_ll_lambda <- numeric(length(lambda_grid))
for (i in seq_along(lambda_grid)) {
profile_fit <- optim(
par = mle[-4],
fn = function(p) llkkw(c(p[1], p[2], p[3], lambda_grid[i]), data),
method = "Nelder-Mead"
)
profile_ll_lambda[i] <- -profile_fit$value
}
# 95% confidence threshold
chi_crit <- qchisq(0.95, df = 1)
threshold <- max(profile_ll_alpha) - chi_crit / 2
# Plot all profiles
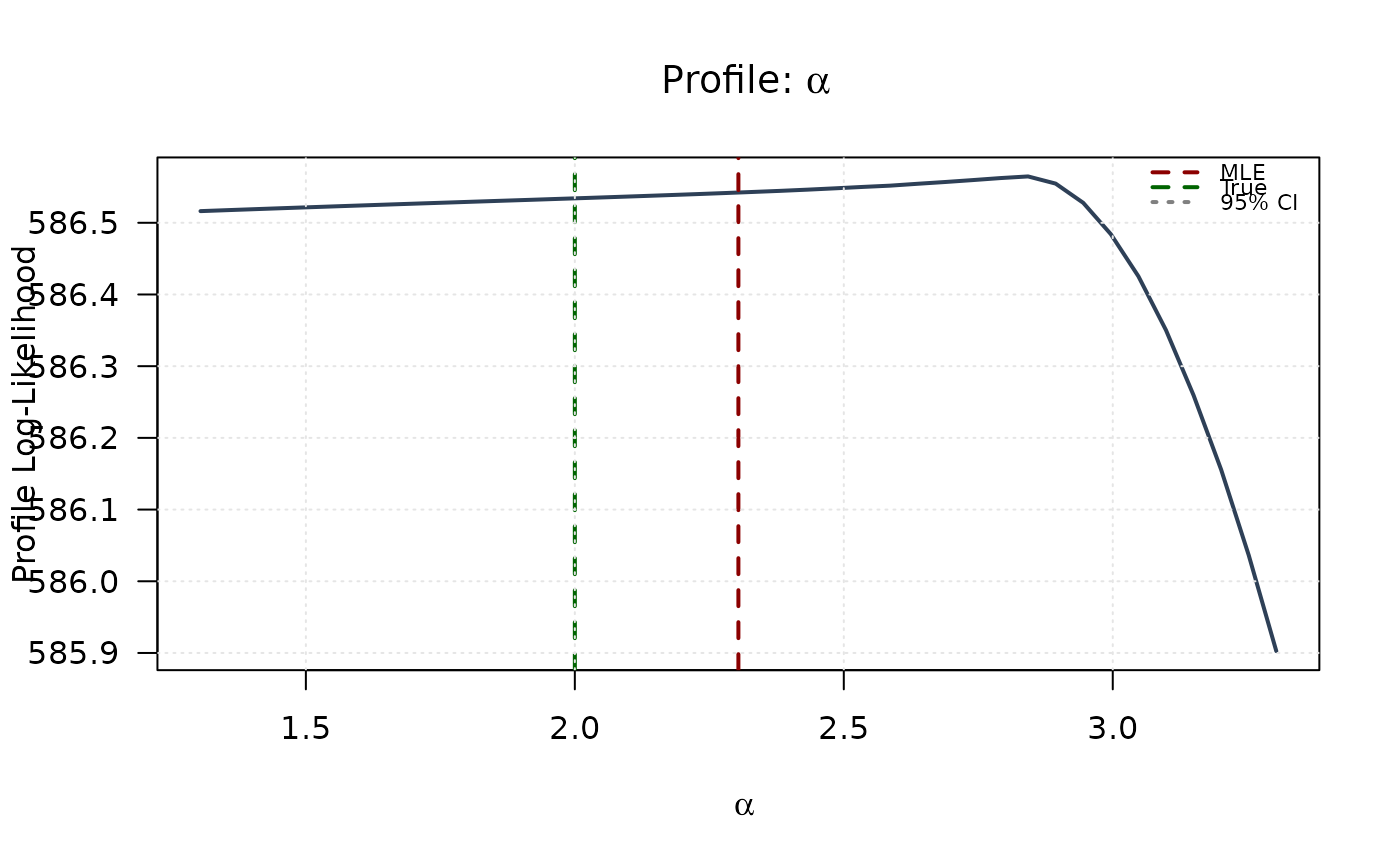
plot(alpha_grid, profile_ll_alpha,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(alpha), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", alpha)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[1], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[1], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
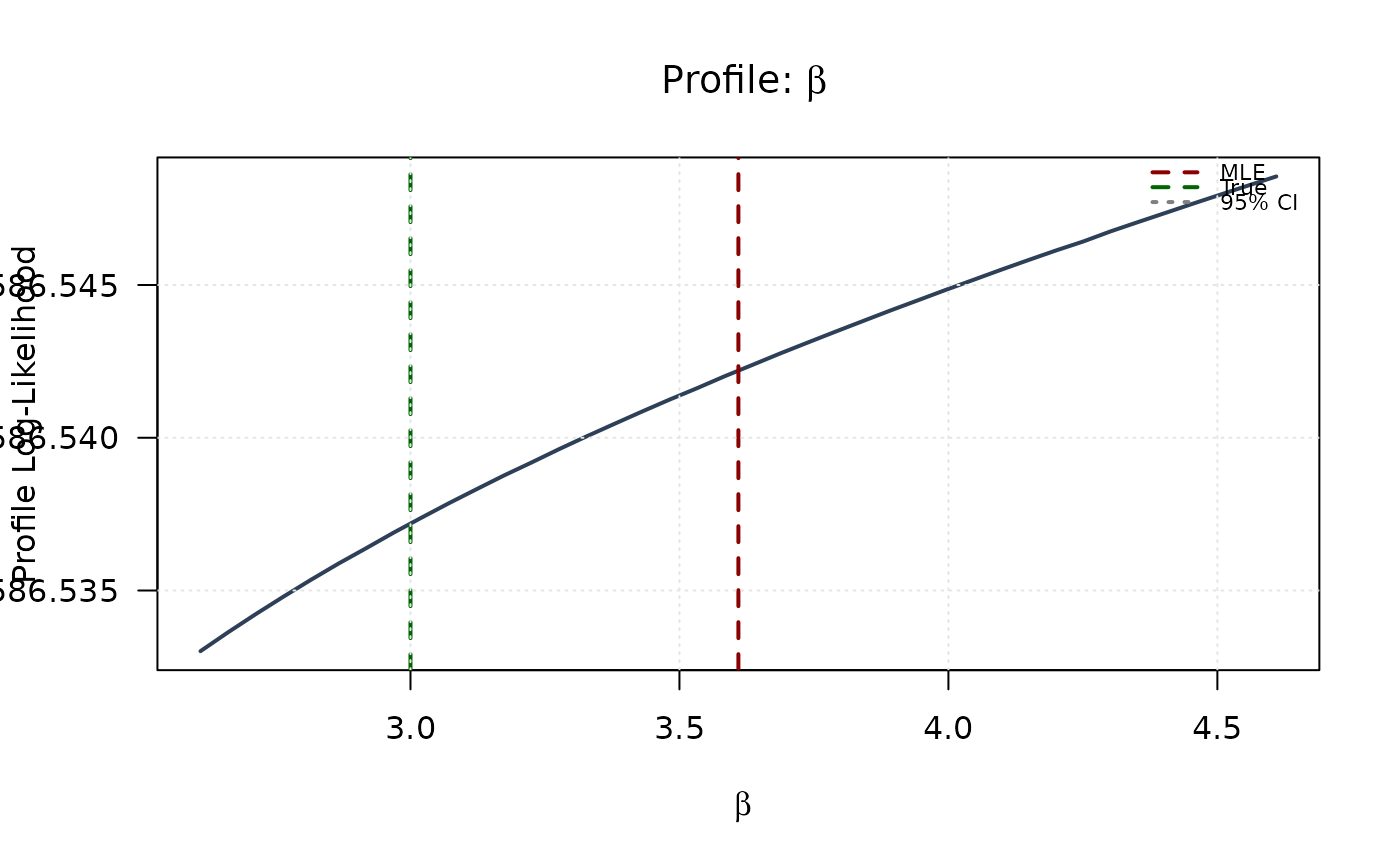
 plot(beta_grid, profile_ll_beta,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(beta), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", beta)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[2], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[2], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
plot(beta_grid, profile_ll_beta,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(beta), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", beta)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[2], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[2], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
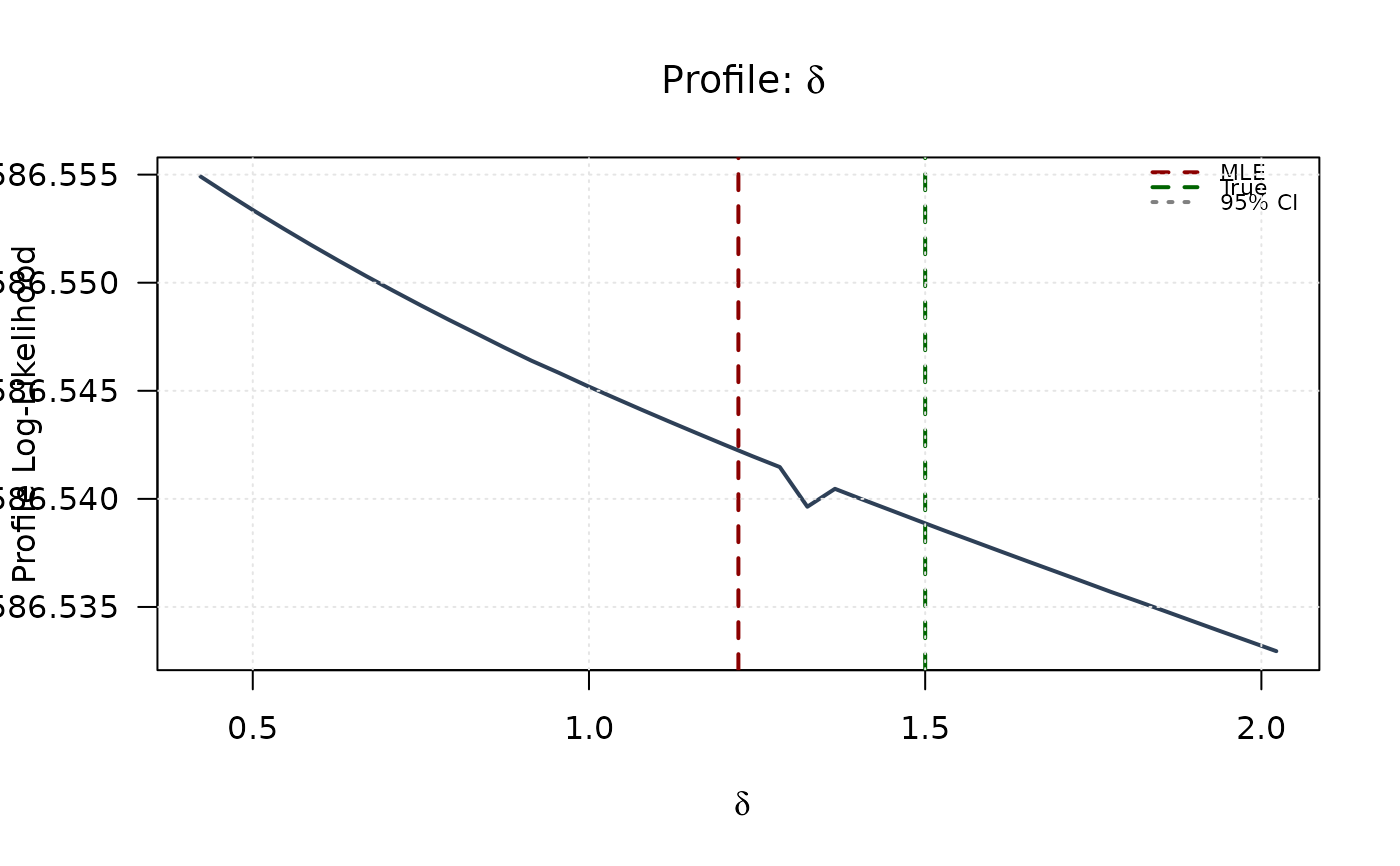
 plot(delta_grid, profile_ll_delta,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(delta), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", delta)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[3], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[3], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
plot(delta_grid, profile_ll_delta,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(delta), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", delta)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[3], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[3], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
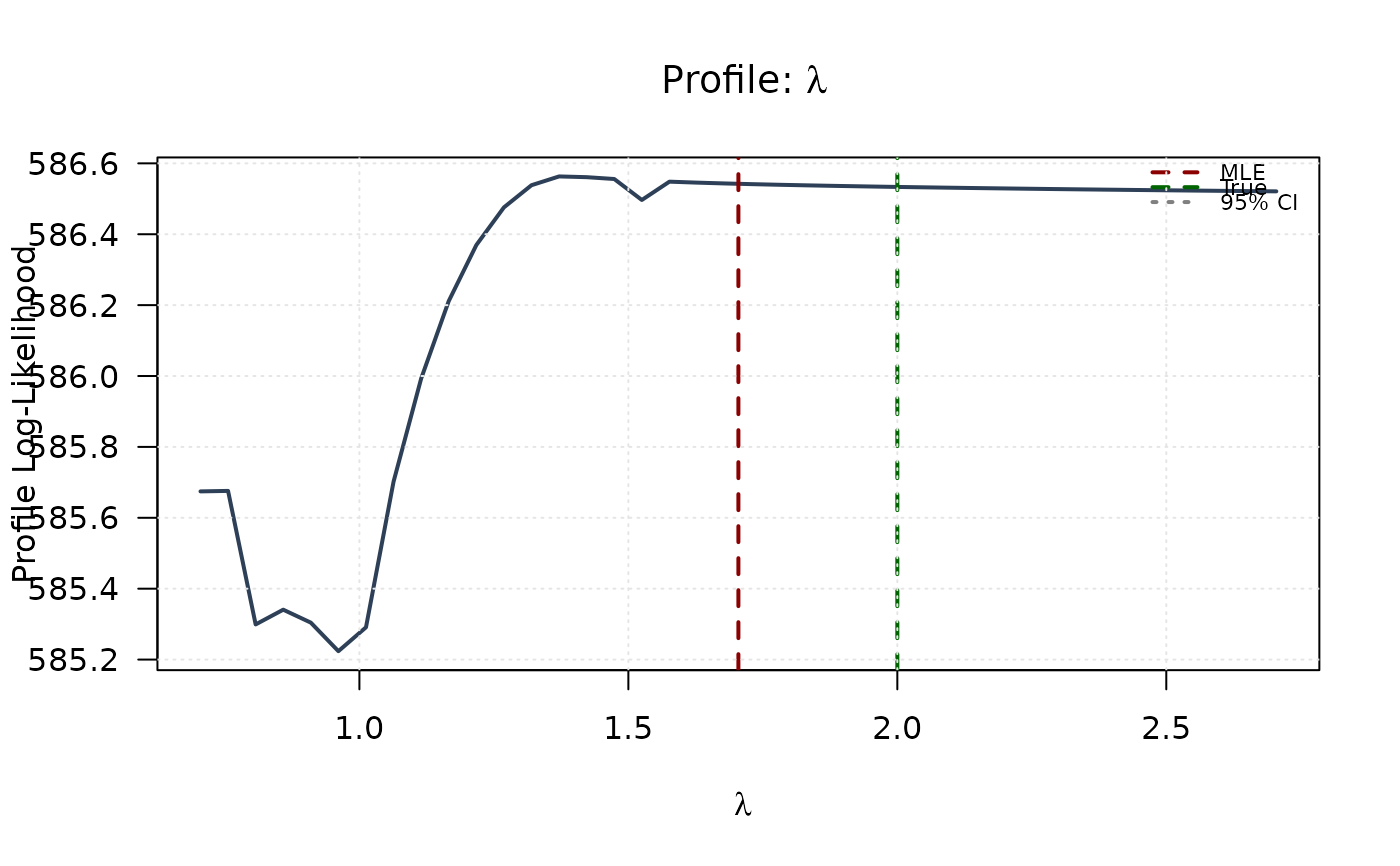
 plot(lambda_grid, profile_ll_lambda,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(lambda), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", lambda)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[4], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[4], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
plot(lambda_grid, profile_ll_lambda,
type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "#2E4057",
xlab = expression(lambda), ylab = "Profile Log-Likelihood",
main = expression(paste("Profile: ", lambda)), las = 1
)
abline(v = mle[4], col = "#8B0000", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = true_params[4], col = "#006400", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(h = threshold, col = "#808080", lty = 3, lwd = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "95% CI"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#808080"),
lty = c(2, 2, 3), lwd = 2, bty = "n", cex = 0.7
)
grid(col = "gray90")
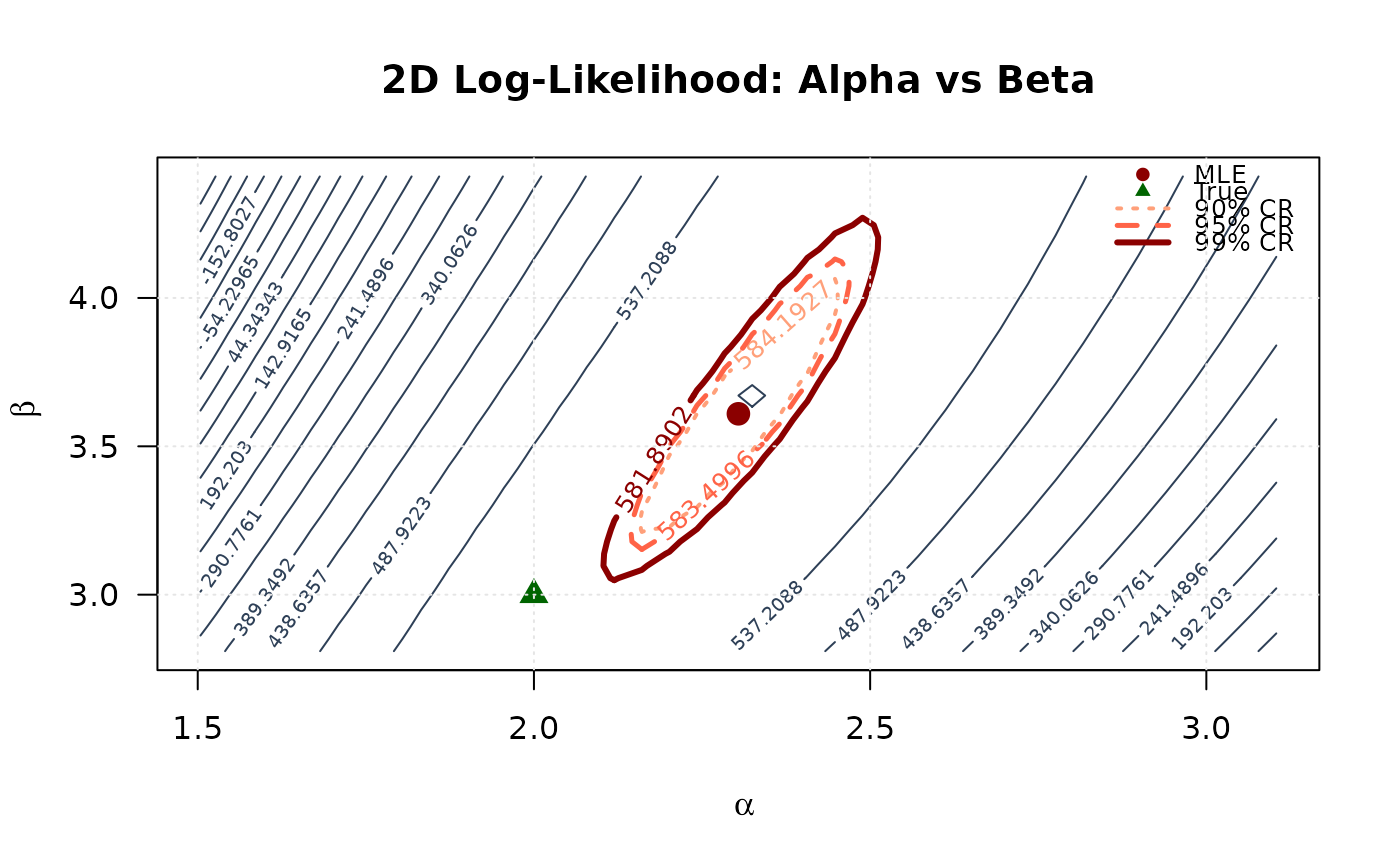
 ## Example 6: 2D Log-Likelihood Surface (Alpha vs Beta)
# Create 2D grid
alpha_2d <- seq(mle[1] - 0.8, mle[1] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
beta_2d <- seq(mle[2] - 0.8, mle[2] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
alpha_2d <- alpha_2d[alpha_2d > 0]
beta_2d <- beta_2d[beta_2d > 0]
# Compute log-likelihood surface
ll_surface <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(alpha_2d), ncol = length(beta_2d))
for (i in seq_along(alpha_2d)) {
for (j in seq_along(beta_2d)) {
ll_surface[i, j] <- -llkkw(c(alpha_2d[i], beta_2d[j], mle[3], mle[4]), data)
}
}
# Confidence region levels
max_ll <- max(ll_surface, na.rm = TRUE)
levels_90 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.90, df = 2) / 2
levels_95 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.95, df = 2) / 2
levels_99 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.99, df = 2) / 2
# Plot contour
contour(alpha_2d, beta_2d, ll_surface,
xlab = expression(alpha), ylab = expression(beta),
main = "2D Log-Likelihood: Alpha vs Beta",
levels = seq(min(ll_surface, na.rm = TRUE), max_ll, length.out = 20),
col = "#2E4057", las = 1, lwd = 1
)
contour(alpha_2d, beta_2d, ll_surface,
levels = c(levels_90, levels_95, levels_99),
col = c("#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
lwd = c(2, 2.5, 3), lty = c(3, 2, 1),
add = TRUE, labcex = 0.8
)
points(mle[1], mle[2], pch = 19, col = "#8B0000", cex = 1.5)
points(true_params[1], true_params[2], pch = 17, col = "#006400", cex = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "90% CR", "95% CR", "99% CR"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
pch = c(19, 17, NA, NA, NA),
lty = c(NA, NA, 3, 2, 1),
lwd = c(NA, NA, 2, 2.5, 3),
bty = "n", cex = 0.8
)
grid(col = "gray90")
## Example 6: 2D Log-Likelihood Surface (Alpha vs Beta)
# Create 2D grid
alpha_2d <- seq(mle[1] - 0.8, mle[1] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
beta_2d <- seq(mle[2] - 0.8, mle[2] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
alpha_2d <- alpha_2d[alpha_2d > 0]
beta_2d <- beta_2d[beta_2d > 0]
# Compute log-likelihood surface
ll_surface <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(alpha_2d), ncol = length(beta_2d))
for (i in seq_along(alpha_2d)) {
for (j in seq_along(beta_2d)) {
ll_surface[i, j] <- -llkkw(c(alpha_2d[i], beta_2d[j], mle[3], mle[4]), data)
}
}
# Confidence region levels
max_ll <- max(ll_surface, na.rm = TRUE)
levels_90 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.90, df = 2) / 2
levels_95 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.95, df = 2) / 2
levels_99 <- max_ll - qchisq(0.99, df = 2) / 2
# Plot contour
contour(alpha_2d, beta_2d, ll_surface,
xlab = expression(alpha), ylab = expression(beta),
main = "2D Log-Likelihood: Alpha vs Beta",
levels = seq(min(ll_surface, na.rm = TRUE), max_ll, length.out = 20),
col = "#2E4057", las = 1, lwd = 1
)
contour(alpha_2d, beta_2d, ll_surface,
levels = c(levels_90, levels_95, levels_99),
col = c("#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
lwd = c(2, 2.5, 3), lty = c(3, 2, 1),
add = TRUE, labcex = 0.8
)
points(mle[1], mle[2], pch = 19, col = "#8B0000", cex = 1.5)
points(true_params[1], true_params[2], pch = 17, col = "#006400", cex = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "90% CR", "95% CR", "99% CR"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
pch = c(19, 17, NA, NA, NA),
lty = c(NA, NA, 3, 2, 1),
lwd = c(NA, NA, 2, 2.5, 3),
bty = "n", cex = 0.8
)
grid(col = "gray90")
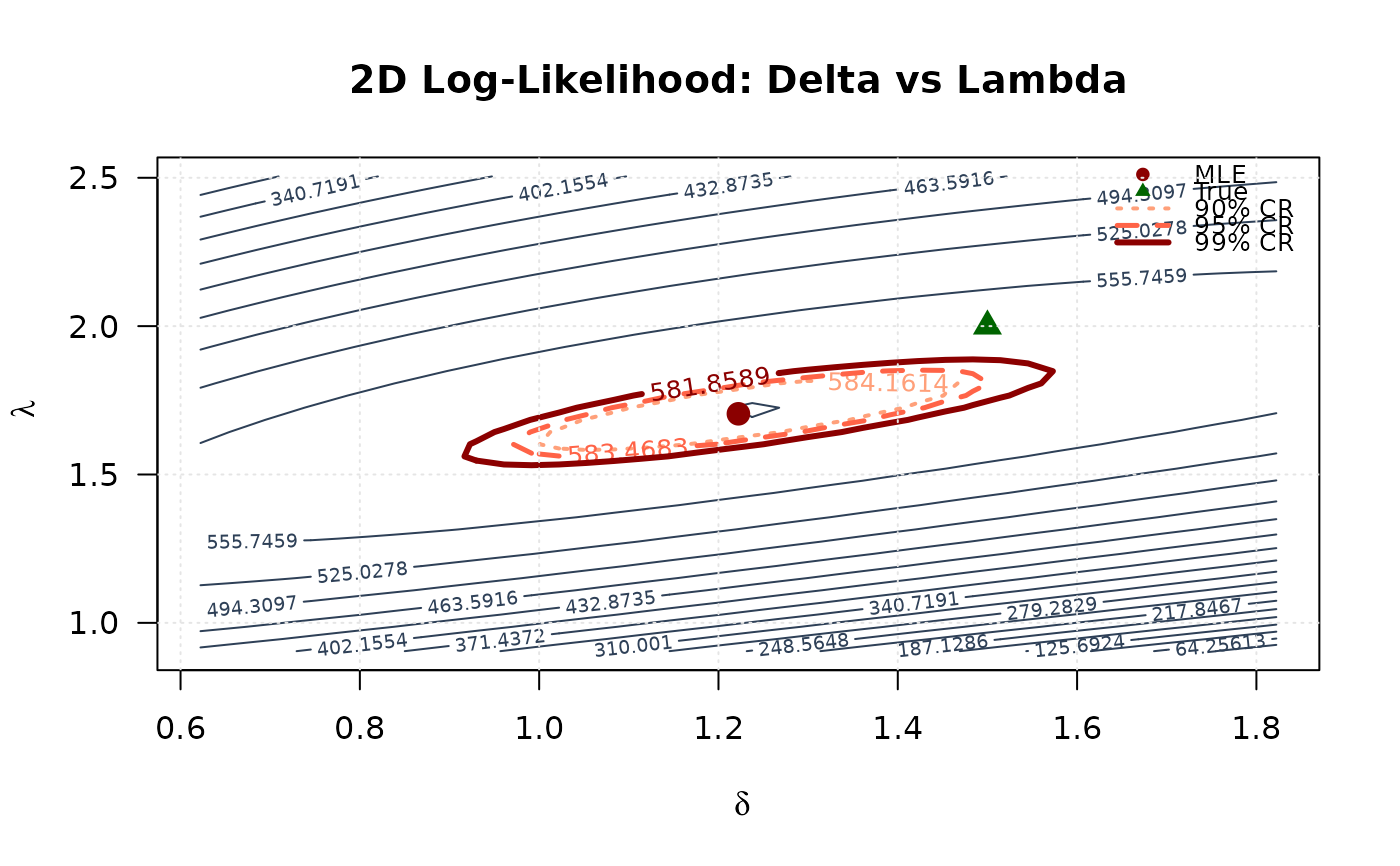
 ## Example 7: 2D Log-Likelihood Surface (Delta vs Lambda)
# Create 2D grid
delta_2d <- seq(mle[3] - 0.6, mle[3] + 0.6, length.out = round(n / 25))
lambda_2d <- seq(mle[4] - 0.8, mle[4] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
delta_2d <- delta_2d[delta_2d > 0]
lambda_2d <- lambda_2d[lambda_2d > 0]
# Compute log-likelihood surface
ll_surface2 <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(delta_2d), ncol = length(lambda_2d))
for (i in seq_along(delta_2d)) {
for (j in seq_along(lambda_2d)) {
ll_surface2[i, j] <- -llkkw(c(mle[1], mle[2], delta_2d[i], lambda_2d[j]), data)
}
}
# Confidence region levels
max_ll2 <- max(ll_surface2, na.rm = TRUE)
levels2_90 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.90, df = 2) / 2
levels2_95 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.95, df = 2) / 2
levels2_99 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.99, df = 2) / 2
# Plot contour
contour(delta_2d, lambda_2d, ll_surface2,
xlab = expression(delta), ylab = expression(lambda),
main = "2D Log-Likelihood: Delta vs Lambda",
levels = seq(min(ll_surface2, na.rm = TRUE), max_ll2, length.out = 20),
col = "#2E4057", las = 1, lwd = 1
)
contour(delta_2d, lambda_2d, ll_surface2,
levels = c(levels2_90, levels2_95, levels2_99),
col = c("#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
lwd = c(2, 2.5, 3), lty = c(3, 2, 1),
add = TRUE, labcex = 0.8
)
points(mle[3], mle[4], pch = 19, col = "#8B0000", cex = 1.5)
points(true_params[3], true_params[4], pch = 17, col = "#006400", cex = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "90% CR", "95% CR", "99% CR"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
pch = c(19, 17, NA, NA, NA),
lty = c(NA, NA, 3, 2, 1),
lwd = c(NA, NA, 2, 2.5, 3),
bty = "n", cex = 0.8
)
grid(col = "gray90")
## Example 7: 2D Log-Likelihood Surface (Delta vs Lambda)
# Create 2D grid
delta_2d <- seq(mle[3] - 0.6, mle[3] + 0.6, length.out = round(n / 25))
lambda_2d <- seq(mle[4] - 0.8, mle[4] + 0.8, length.out = round(n / 25))
delta_2d <- delta_2d[delta_2d > 0]
lambda_2d <- lambda_2d[lambda_2d > 0]
# Compute log-likelihood surface
ll_surface2 <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(delta_2d), ncol = length(lambda_2d))
for (i in seq_along(delta_2d)) {
for (j in seq_along(lambda_2d)) {
ll_surface2[i, j] <- -llkkw(c(mle[1], mle[2], delta_2d[i], lambda_2d[j]), data)
}
}
# Confidence region levels
max_ll2 <- max(ll_surface2, na.rm = TRUE)
levels2_90 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.90, df = 2) / 2
levels2_95 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.95, df = 2) / 2
levels2_99 <- max_ll2 - qchisq(0.99, df = 2) / 2
# Plot contour
contour(delta_2d, lambda_2d, ll_surface2,
xlab = expression(delta), ylab = expression(lambda),
main = "2D Log-Likelihood: Delta vs Lambda",
levels = seq(min(ll_surface2, na.rm = TRUE), max_ll2, length.out = 20),
col = "#2E4057", las = 1, lwd = 1
)
contour(delta_2d, lambda_2d, ll_surface2,
levels = c(levels2_90, levels2_95, levels2_99),
col = c("#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
lwd = c(2, 2.5, 3), lty = c(3, 2, 1),
add = TRUE, labcex = 0.8
)
points(mle[3], mle[4], pch = 19, col = "#8B0000", cex = 1.5)
points(true_params[3], true_params[4], pch = 17, col = "#006400", cex = 1.5)
legend("topright",
legend = c("MLE", "True", "90% CR", "95% CR", "99% CR"),
col = c("#8B0000", "#006400", "#FFA07A", "#FF6347", "#8B0000"),
pch = c(19, 17, NA, NA, NA),
lty = c(NA, NA, 3, 2, 1),
lwd = c(NA, NA, 2, 2.5, 3),
bty = "n", cex = 0.8
)
grid(col = "gray90")
 # }
# }